Neuroendocrine Cancer
The neuroendocrine system is an essential part of the body’s hormonal network, and neuroendocrine cancer is a complex disorder that is often misdiagnosed and misunderstood. We examine all the key aspects of neuroendocrine cancer in this complete overview, including symptoms, diagnosis, available treatments, and current research.
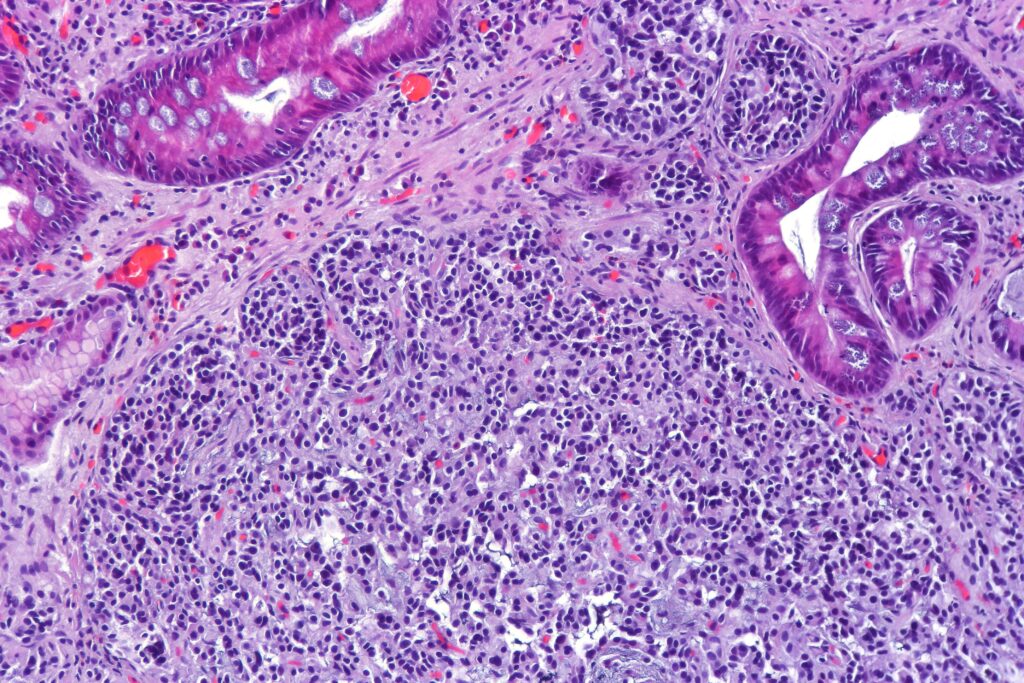
The Basics of Neuroendocrine Cancer:
Neuroendocrine cells that produce hormones are the source of neuroendocrine cancer. The lungs, pancreas and gastrointestinal system are some of the body organs that contain these cells. These cells develop abnormally, resulting in tumor formation and neuroendocrine cancer.
Types of Neuroendocrine Tumors:
Neuroendocrine tumors are not created equal. They can be divided into several categories based on where they live and how they behave. The major types are neuroendocrine tumors of the pancreas, carcinoid tumors, and small and large-cell neuroendocrine carcinomas. Identifying the particular type is necessary to create a customized treatment strategy.
Symptoms and Diagnosis:
Neuroendocrine cancer presents with a variety of symptoms, such as redness of the skin, diarrhea, abdominal discomfort, and hormonal abnormalities, making it difficult to detect early. Sometimes a biopsy may be necessary in addition to blood tests and imaging examinations for an accurate diagnosis. The key to improving treatment outcomes is early detection.
Treatment Options:
The type, location, and stage of the tumor all influence the therapy strategy for neuroendocrine cancer. Common treatments include surgery, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy. Additionally, peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) and somatostatin analogs have emerged as viable alternatives that provide more personalized and focused treatment plans.
Living with Neuroendocrine Cancer:
Along with medical treatment, lifestyle changes and emotional support are also essential for neuroendocrine cancer survivors. It is important to educate patients and their families about the value of a multidisciplinary approach that may include frequent monitoring of hormone imbalances, psychological support, and dietary counseling.
Research and Innovations:
Neuroendocrine cancer research is a dynamic topic with ongoing efforts to understand the underlying causes of the disease and discover new treatment options. Stay up-to-date on the latest advances, as scientific discoveries may provide hope for a better prognosis and a higher quality of life for people with neuroendocrine cancer.
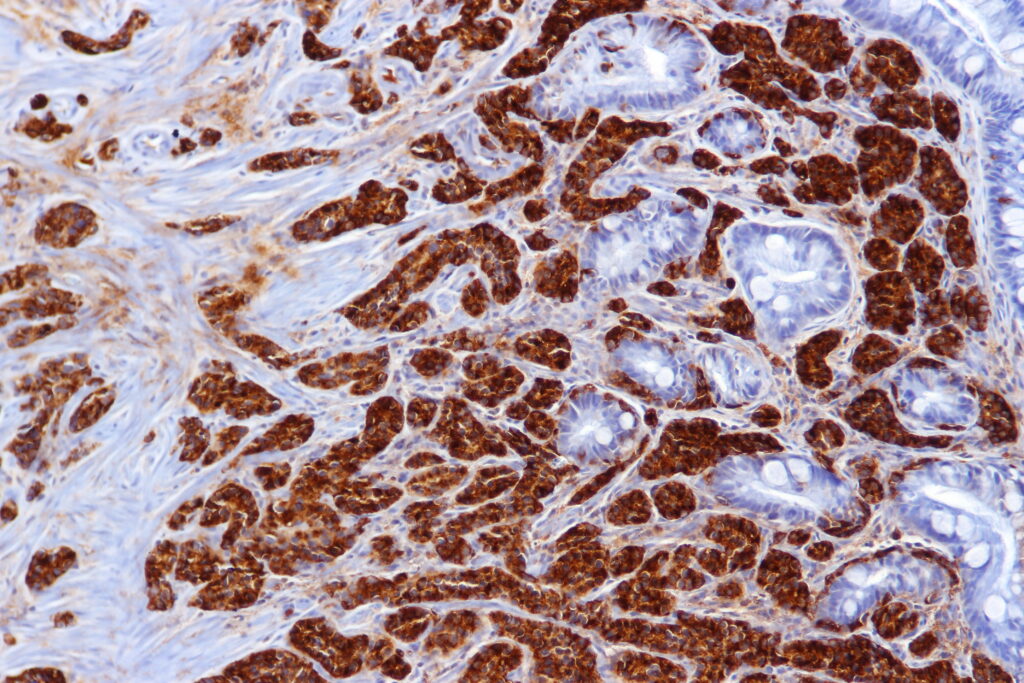
Conclusion:
The challenges of neuroendocrine cancer vary, but patients can face these obstacles with greater resilience if they have complete information about the condition, are diagnosed early, and receive cutting-edge therapy. Improvements in outcomes and support for people affected by neuroendocrine cancer can be achieved through raising awareness and encouraging further research.
Table of Contents
FAQ’S-
What is neuroendocrine cancer?
Neuroendocrine cells, which combine the properties of nerve and hormone-producing cells, are the source of neuroendocrine cancer, an uncommon form of cancer. These tumors can grow in multiple organs and can be nonfunctional (meaning they do not produce hormones) or functional, meaning they can affect health by causing hormone imbalance, metastasis, and other problems.
How does neuroendocrine cancer kill you?
Neuroendocrine cancer carries a high risk of life-threatening side effects and major health consequences. The impact on a person’s health depends on several factors, such as tumor size, location, functionality (i.e., hormone production), and stage at diagnosis.
The following are some of the ways in which neuroendocrine cancer can be fatal:
Metastasis: It is possible for neuroendocrine tumors to spread to other body areas. When cancer cells invade vital tissues or organs, they can disrupt regular operations, resulting in malfunction and eventual organ failure.
Hormonal imbalance: The excessive production of hormones produced by functional neuroendocrine tumors can result in a number of problems. For example, excessive insulin production by neuroendocrine tumors of the pancreas can result in hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, which can be fatal if untreated.
Bleeding and blockage: GIT tumors, especially those affecting the small intestine, have the potential to obstruct or block the digestive system. These tumors can also cause bleeding, which can have negative consequences such as anemia.
Liver involvement: Neuroendocrine tumors often metastasize to the liver. Since the liver is an essential organ that performs many functions including metabolism and detoxification, large-scale cancer cell involvement can result in liver failure.
Cardiovascular difficulties: Neuroendocrine tumors have the potential to produce compounds that affect the heart, which may result in cardiac difficulties. Heart valve damage caused by long-term carcinoid syndrome is known as carcinoid heart disease, an uncommon but dangerous disorder.
Treatment-related issues: Radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and surgery are some treatments for neuroendocrine cancer that may have side effects or problems. These issues can sometimes pose a complete threat to a person’s health.
It is important to remember that outcomes can vary greatly and not every person with neuroendocrine cancer will suffer potentially fatal outcomes. For many people with neuroendocrine tumors, the prognosis has improved due to advances in medical research and treatment options. Nonetheless, the severity of the disease and its impact on well-being are dependent on individual circumstances, and optimal outcomes still depend on timely identification and appropriate medical support.